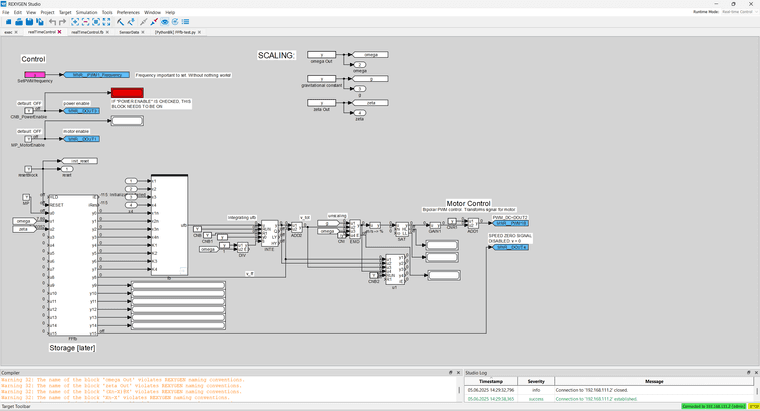
I am not sure how to make the stop in the lower right hand corner run

I am not sure how to make the stop in the lower right hand corner run
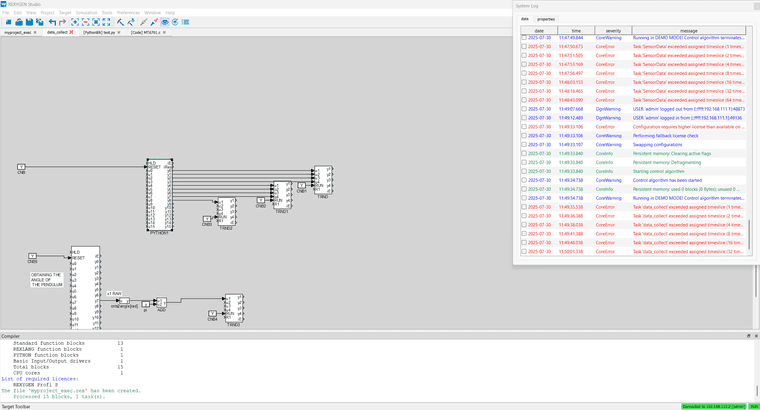
I am not quite sure what this error means or how to fix it if any knows
Hi I am trying to find a way to get my bluetooth sensor(Witmotion WT9011DCL 9-axis BLE Magnetometer Gyroscope) to communiate with rerxygen so I can stream the data into rexygen. I have been able to connect the sensor with my raspberry Pi 4 monacrohat. I then tried to stream the data into rexygen but have been unable to do so. I have attached the my program below. 
# coding:UTF-8
import asyncio
import bleak
from PyRexExt import REX
class DeviceModel:
def __init__(self, deviceName, BLEDevice, callback_method):
self.deviceName = deviceName
self.BLEDevice = BLEDevice
self.client = None
self.writer_characteristic = None
self.isOpen = False
self.callback_method = callback_method
self.TempBytes = []
async def openDevice(self):
try:
async with bleak.BleakClient(self.BLEDevice, timeout=15) as client:
self.client = client
self.isOpen = True
print("Device connected.")
REX.y9.v = 1 # Connected
target_service_uuid = "0000ffe5-0000-1000-8000-00805f9a34fb"
target_characteristic_uuid_read = "0000ffe4-0000-1000-8000-00805f9a34fb"
target_characteristic_uuid_write = "0000ffe9-0000-1000-8000-00805f9a34fb"
notify_characteristic = None
for service in client.services:
if service.uuid == target_service_uuid:
for char in service.characteristics:
if char.uuid == target_characteristic_uuid_read:
notify_characteristic = char
if char.uuid == target_characteristic_uuid_write:
self.writer_characteristic = char
if self.writer_characteristic:
await self.sendData([0xFF, 0xAA, 0x24, 0x01, 0x00]) # 6-axis mode
await self.sendData([0xFF, 0xAA, 0x03, 0x09, 0x00]) # 100 Hz
if notify_characteristic:
await client.start_notify(notify_characteristic.uuid, self.onDataReceived)
while self.isOpen:
await asyncio.sleep(1)
await client.stop_notify(notify_characteristic.uuid)
else:
print("Notify characteristic not found.")
REX.y9.v = 2 # Failed
except Exception as e:
print("BLE connection failed:", e)
REX.y9.v = 2 # Failed
def onDataReceived(self, sender, data):
bytes_list = list(data)
self.TempBytes.extend(bytes_list)
if len(self.TempBytes) >= 20:
if self.TempBytes[0] == 0x55 and self.TempBytes[1] == 0x61:
self.processData(self.TempBytes[:20])
self.TempBytes = []
def processData(self, Bytes):
def get_val(low, high, scale):
raw = (high << 8) | low
val = raw - 65536 if raw >= 32768 else raw
return round(val / 32768 * scale, 3)
acc_x = get_val(Bytes[2], Bytes[3], 16)
acc_y = get_val(Bytes[4], Bytes[5], 16)
acc_z = get_val(Bytes[6], Bytes[7], 16)
gyro_x = get_val(Bytes[8], Bytes[9], 2000)
gyro_y = get_val(Bytes[10], Bytes[11], 2000)
gyro_z = get_val(Bytes[12], Bytes[13], 2000)
ang_x = get_val(Bytes[14], Bytes[15], 180)
ang_y = get_val(Bytes[16], Bytes[17], 180)
ang_z = get_val(Bytes[18], Bytes[19], 180)
# Send to REXYGEN outputs
REX.y0.v = acc_x
REX.y1.v = acc_y
REX.y2.v = acc_z
REX.y3.v = gyro_x
REX.y4.v = gyro_y
REX.y5.v = gyro_z
REX.y6.v = ang_x
REX.y7.v = ang_y
REX.y8.v = ang_z
print("Data:", acc_x, acc_y, acc_z, gyro_x, gyro_y, gyro_z, ang_x, ang_y, ang_z)
async def sendData(self, data):
try:
if self.client and self.writer_characteristic:
await self.client.write_gatt_char(self.writer_characteristic.uuid, bytes(data))
except Exception as e:
print("Write failed:", e)
class BLEScanner:
def __init__(self, target_mac="CC:0E:4F:3B:A4:3B"):
self.target_mac = target_mac
self.BLEDevice = None
self.device_model = None
async def scan_and_connect(self):
try:
print("Scanning for BLE devices...")
devices = await bleak.BleakScanner.discover(timeout=10.0)
for d in devices:
if d.address == self.target_mac:
self.BLEDevice = d
break
if not self.BLEDevice:
print("Target device not found.")
REX.y9.v = 2
return
self.device_model = DeviceModel("MyBLE", self.BLEDevice, None)
await self.device_model.openDevice()
except Exception as e:
print("Scan or connect error:", e)
REX.y9.v = 2
def run_ble_task():
loop = asyncio.new_event_loop()
asyncio.set_event_loop(loop)
scanner = BLEScanner()
loop.run_until_complete(scanner.scan_and_connect())
loop.close()
# Main entry point for REXYGEN
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Starting REXYGEN BLE program")
REX.y9.v = 2 # Default = failed
run_ble_task()
Hi I am trying to connect my bluetooth sensor(Witmotion WT9011DCL 9-axis BLE Magnetometer Gyroscope) to rexygen via bluetooth so I can stream the data from the sensor into rexygen. I am not sure how to get started on this.
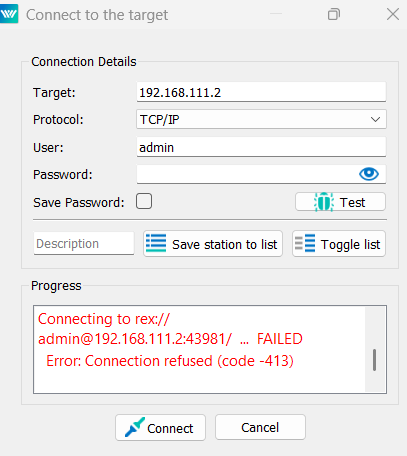
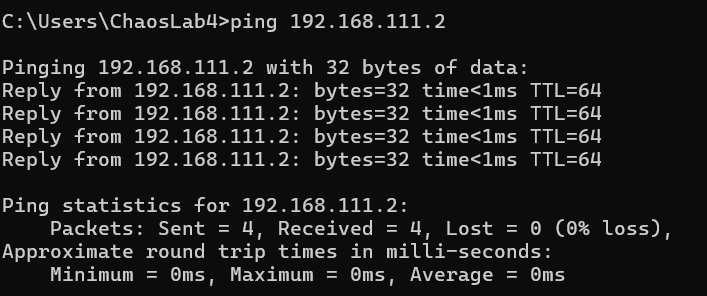
I am unable to conneect to the rexygen to my Raspberry Pi.
@cechurat Hi Thomas when I hover my mouse over the error I get this message.
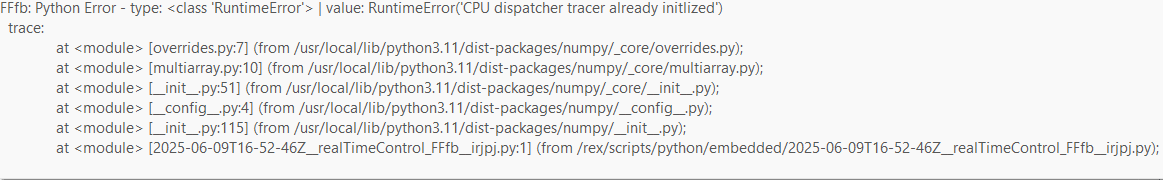
I am not quite sure what it means or how to fix it
@cechurat 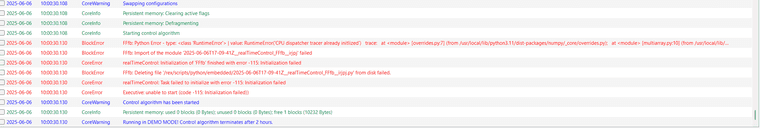
I think the problem might be in the python block.
import numpy as np
import time
from numpy import sin,cos,pi
from scipy.integrate import solve_ivp, solve_bvp, quad, odeint
from scipy.linalg import solve_continuous_are
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
#import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PyRexExt import REX
def init():
global ω,ζ,π,τ,τ1,τpred,xmax,umax,θinti,θdotinit,xinit,xdotinit,xstate_init,θend1,θend2,θdotend,xend,xdotend,xstate_end1,xstate_end2,Q,R,ts,dt,ts1,bvpfcn,bcfcn,ff,uff0,uff,runningCost,A,B,mRiccati,Sall,Ball,Kall,fpred,us,j
global xstate_end,FFsol,X,uff,vs,Kvec,Xlast,Klast
############################################ Define parameters
ω = REX.u1.v
ζ = REX.u2.v; # pendulum friction (scaled: 1 = critical damping)
π = pi; # π = 3.14159...
τ = 2*π # swingup time = 1 period, in scaled units
τpred = 1 # allow for calculation time, in scaled units
τ1 = 2*τ # for sim: swingup + balance time
xmax = 2; # track limits at ±xmax
umax = 5; # clip u for simulation test ONLY (not design)
θinit = 0; # initial angle of pendulum
θdotinit = 0.0; # initial angular velocity of pendulum
xinit = 0.0; # initial position of cart
xdotinit = 0.0; # initial velocity of cart
xstate_init = np.array([θinit,θdotinit,xinit,xdotinit]) # eventually, from expt.
θend1 = π # CCW swingup, assume θinit ∊ (-π,π)
θend2 = -π # CW swingup
θdotend = 0.0; # final angular velocity of pendulum
xend = 0.0 * xmax; # final cart position
xdotend = 0.0; # final cart velocity
xstate_end1 = np.array([θend1,θdotend,xend,xdotend]) # modify for swing down, transport, ...
xstate_end2 = np.array([θend2,θdotend,xend,xdotend]) # modify for swing down, transport, ...
Q = np.diag([1,10,1,1]) # weighting for states for LQR
R = np.array([10]) # weighting for input for LQR
ts = np.arange(0, τ, 0.01*ω) # swing up in τ
dt = 0.01*ω
ts1 = np.arange(0, τ1, 0.01*ω) # swing up in τ, balance for another τ
############################################# Define functions
def bvpfcn(t, X): # solve coupled state-adjoint system
θ, θdot, x, xdot, λθ, λθdot, λx, λxdot = X
dX = np.zeros((8, X.shape[1])) # array dimension is 8 * nx
sinθ = sin(θ); cosθ = cos(θ)
u = -λxdot + λθdot*cosθ
dX[0] = θdot
dX[1] = -sinθ - u*cosθ
dX[2] = xdot
dX[3] = u
dX[4] = λθdot * (cosθ - u*sinθ)
dX[5] = - λθ
# dX[6] = -x**3 / xmax**4 # or: from running cost term (x/xmax)**4
dX[6] = 0 # running cost independent of x
dX[7] = -λx
return dX # Return derivatives (array)
def bcfcn(x0, xτ): # boundary conditions for 4d-state at t = 0, τ
dx0 = x0[0:4] - xstate_init # boundary condition for 4d state at t=0
dxτ = xτ[0:4] - xstate_end # bc at t=τ
return np.hstack((dx0,dxτ)) # 8-dim vector for solve_bvp
def ff(x0,xτ,τ): # ff state x0 → xτ in τ
θinit,_,xinit,_ = x0
θend, _,xend, _ = xτ
nt = 21 # number of time points, to start
tvec = np.linspace(0, τ, nt)
xλguess = np.zeros((8, nt)) # initial guesses for state trajectories
xλguess[0, :] = np.linspace(θinit, θend, num=nt) # θ linear, θinit → θend
xλguess[2, :] = np.linspace(xinit, xend, num=nt) # x linear, xinit → xend
FFsol = solve_bvp(bvpfcn, bcfcn, tvec, xλguess, tol=0.1) # solve boundary-value problem
return FFsol.sol
def uff0(t): # feedforward acceleration (cannot evaluate on arrays)
θ,_,_,_,_,λθdot,_,λxdot = FFsol(t) # evaluate interp funcs at time=t
uff0 = -λxdot + λθdot*cos(θ) if t<τ else 0
return uff0
uff = np.vectorize(uff0) # define vectorized version (can call with array)
def runningCost(t): # to calc cost of the feedforward command
return 0.5*uff0(t)**2
def A(t): # dynamical matrix (local linear, nominal)
θ = FFsol(t)[0] # FFsol from FF function
Amat = np.zeros((4,4)) # 4 is from xstate.shape[0]
Amat[0,1] = 1
Amat[1,0] = -cos(θ) + uff(t)*sin(θ)
Amat[1,1] = 0
Amat[2,3] = 1
return Amat # evaluated at time t
def B(t): # input vector (local linear, nominal)
θ = FFsol(t)[0] # FFsol from FF function
Bmat = np.zeros((4,1)) # 4 is from xstate.shape[0]
Bmat[1] = -cos(θ)
Bmat[3] = 1
return Bmat
def mRiccati(t,S): # derivatives for matrix Riccati (vector form)
Smat = S.reshape((4,4)) # convert 16 vector to 4x4 matrix
A0 = A(t) # current dynamical matrix
B0 = B(t) # current input vector
dSmat = - A0.T @ Smat - Smat @ A0 - Q + Smat @ (B0 @ B0.T) @ Smat / R[0]
dS = dSmat.reshape((16)) # convert 4x4 matrix to 16 vector
return dS
def Sall(Send,τ,tvec): # S matrix evaluated at times tvec
Send1 = Send.reshape((16))
t_span = (τ, 0) # solve backwards in time, from τ → 0
Ssol1 = solve_ivp(mRiccati, t_span, Send1, dense_output=True).sol
return Ssol1(tvec).reshape(4,4,tvec.size) # evaluate on tvec
def Ball(FFsol,tvec): # input matrix (local linear, nominal)
θ = FFsol(tvec)[0]
nt = tvec.size
Bmat = np.zeros((4,nt)) # 4 is from xstate.shape[0]
Bmat[1] = -cos(θ)
Bmat[3] = np.ones((nt))
return Bmat
def Kall(Send,FFsol,τ,tvec): # for graphing
tvec1 = np.clip(tvec, 0, τ) # elements beyond ff range are clipped to limits
S = Sall(Send,τ,tvec1) # 4 x 4 x nt matrix (nt copies of 4x4 matrix
B = Ball(FFsol,tvec1) # 4 x nt matrix (nt copies of 4-vector)
return np.einsum('ijk,jk->ik', S, B)/R[0] # sum over inner index, element-mult tvec index
def fpred(t,xstate): # dynamical eqs, for constant-v input
θ, θdot, _, xdot = xstate # dynamical states
dX = np.zeros((4)) # 4 is from xstate.shape[0]
dX[0] = θdot
dX[1] = -sin(θ) - 2*ζ*θdot # sim has pendulum friction, even if ff does not
dX[2] = xdot
dX[3] = 0 # driving term is vtot; utot is a derived variable
return dX
############################################# prediction of future state
xpred = solve_ivp(fpred, (0, τpred), xstate_init, dense_output=True).sol # predict future state
xstate_init = xpred(τpred) # "initial" state, as predicted τpred in future
θ0 = xstate_init[0]; # extrapolated θ0 might not be ∊ (-π,π)
θ1 = (θ0+π) % (2*π) - π # modulus 2π
xstate_init[0] = θ1 # new angle is ∊ (-π,π)
############################################# FF calculations
xstate_end = xstate_end1; θend = θend1
FFsol = ff(xstate_init,xstate_end,τ) # ff solution for 4-state and 4-adjoint, 0→τ
FFsol1 = FFsol
Jff1 = 0.5*np.sum(uff(ts)**2)*dt # integrated running cost = overall cost
xstate_end = xstate_end2; θend = θend2
FFsol = ff(xstate_init,xstate_end,τ) # ff solution for 4-state and 4-adjoint, 0→τ
FFsol2 = FFsol
Jff2 = 0.5*np.sum(uff(ts)**2)*dt # integrated running cost = overall cost
REX.y11.v = f"feedforward cost: θend = π, Jff1 = {Jff1:0.2f}, θend = -π, Jff2 = {Jff2:0.2f}"
if (Jff1 < Jff2):
FFsol = FFsol1; xstate_end = xstate_end1
else:
FFsol = FFsol2; xstate_end = xstate_end2
############################################### fb calculations
Aend = A(τ) # linear dynamics A matrix at t=τ
Bend = B(τ) # linear input-coupling B vector at t=τ
Send = solve_continuous_are(Aend,Bend,Q,R) # static S matrix from ARE
Kvec = Kall(Send,FFsol,τ,ts1) # feedback gain vectors for t in ts1
############################################### get arrays
θs,θdot,x, xdot,_,_,_,_ = FFsol(ts)
X = np.array([θs,θdot,x,xdot])
θlast,θdotlast,xlast,xdotlast,_,_,_,_=FFsol(2*π) # Evaluate last values
Xlast = np.array([[θlast],[θdotlast],[xlast],[xdotlast]])
X = np.hstack((X,Xlast)) # add last value
Klast = Kall(Send,FFsol,τ,2*π+0.1)
Kvec = np.hstack((Kvec,Klast))
vs = np.hstack((xdot,0))
j=0
def main():
start_test = time.perf_counter()
global j,X,uff,vs,Kvec
if not REX.u0.v and j == 0:
return
else: REX.y15.v = True
REX.y10.v= f"len(X)={len(X[0])}"
if (j >= len(X[0])):
REX.y8.v = 0
return
# Value for every time
REX.y0.v = X[0][j]
REX.y1.v = X[1][j]
REX.y2.v = X[2][j]
REX.y3.v = X[3][j]
REX.y4.v = Kvec[0][j]
REX.y5.v = Kvec[1][j]
REX.y6.v = Kvec[2][j]
REX.y7.v = Kvec[3][j]
REX.y8.v = vs[j]
j += 1
test_time = time.perf_counter() - start_test
REX.y9.v = f"test time = {test_time:0.3f} s"
return
def exit():
# PUT YOUR CODE HERE
return

I am not sure how to make the stop in the lower right hand corner run